Content
- Test description
- Test sensitivity and cognitive functions necessary for its implementation
- How the test is used in clinical medicine and what conditions it detects
- Test applicability in pharma, alcohol dependence and lack of sleep
- The history of the test
- Conclusions
- References
Test Description
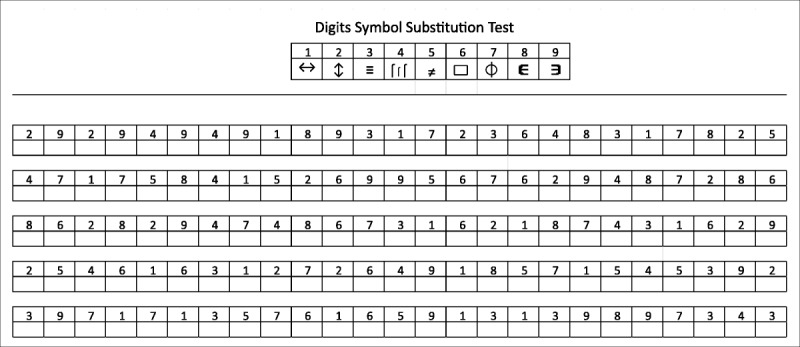
The Digital Symbol Substitution Test (DSST) is used in neuropsychology to detect cognitive deficits. All you need to pass the test is the ability to write. The patient is given a sheet of paper, in the upper part of which a key is written – these are number-symbol pairs. At the bottom of the sheet are empty numbered cells. The patient fills them in with symbols from the key corresponding to the cell number. If the patient repeatedly performs DSST, then the characters in the key are replaced to eliminate the memory effect.
Image source: http://europepmc.org/article/MED/30124583
Typically, the test is given 90 or 120 seconds. DSST results are the number of correctly filled cells in the allotted time. The specialist interprets the result depending on the patient’s age, diseases, and brain damage.
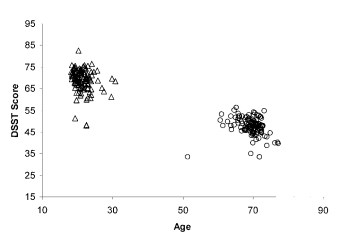
In a meta-analysis, scientists at Syracuse University (USA) summarized the results of testing healthy young people and retirees. The meta-analysis included 141 studies involving 3876 retirees and 3731 young adults. The graph shows that with age, the indicators decrease by about 20 points:
Image source: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/8635540_Adult_Age_and_Digit_Symbol_Substitution_Performance_A_Meta-Analysis
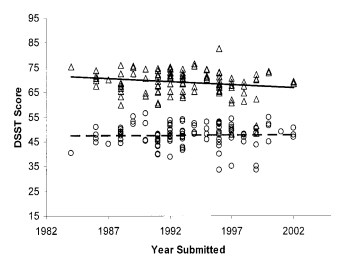
Scientists have calculated how the indicators change over time. It turned out that in the elderly, the performance of DSST increased slightly in the period 1985-2022. Moreover, among young people, on the contrary, it decreased over the same period:
Image source: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/8635540_Adult_Age_and_Digit_Symbol_Substitution_Performance_A_Meta-Analysis
Test Sensitivity and Cognitive Functions Necessary for Its Implementation
The digital symbol substitution test is sensitive to detecting a wide range of acute and chronic cognitive impairments, regardless of their nature or origin. It detects both the very presence of impairments and changes in cognitive function:
- in diseases of the nervous tissue – and reflects the effectiveness of treatment;
- with brain damage – and shows the dynamics and degree of recovery after functional disability;
- with abuse of substances that affect the brain and establish a positive effect when giving up bad habits;
- with age-related changes – and shows the rate of degradation;
- when taking medications – and reflects the time and extent of their impact on cognitive abilities.
This sensitivity of DSST is due to the influence of many brain functions required for testing. The same processes are needed for everyday work tasks, learning and cognition, and social interaction. The test determines the level of attention and reflects the result of the integration of visual signals and mental processes in the brain and their implementation in fine motor skills. Any disruption of the brain reduces the number of correct answers.
Cognitive functions are used to perform DSST:
- working memory to remember the rules of the test;
- associative learning and planning to strategize and not go to the key each time;
- visual functions for eye movement control and image scanning;
- speed of signal processing for speed of movements;
- essential manual dexterity (ability to write or draw);
- the concentration of attention.
How The Test is Used in Clinical Medicine and What Conditions It Detects
The digital character substitution test is most commonly used in modern clinical neuropsychology. It is not influenced by language, culture, or level of education and allows you to determine if the patient has a cognitive deficit quickly. The test is sensitive to cognitive deficits in a wide range of diseases and conditions:
- brain damage;
- mental disorders such as schizophrenia and major depressive disorder;
- cognitive impairment associated with aging.
For example, patients with schizophrenia have low processing speed when going through the DSST. Type 2 diabetes is also associated with an increased risk of mild cognitive impairment and dementia. In both cases, DSST accurately identifies cognitive deficits.
The test is used to evaluate and manage patients. It is an effective method for monitoring brain function, an indicator of the effectiveness of treatment and the speed of recovery. If the patient begins to show better results in the test over time, this helps the doctor understand that the treatment regimen is chosen correctly.
For example, major depressive disorder (MDD) impairs neuropsychological measures of brain executive function. In patients with MDD, the effectiveness of the test decreases by about 2 times. DSST helps you better choose an antidepressant and its dosage. The test also shows that 6 months after discharge from the hospital, patients are functionally restored to solve problems at work, school and home.
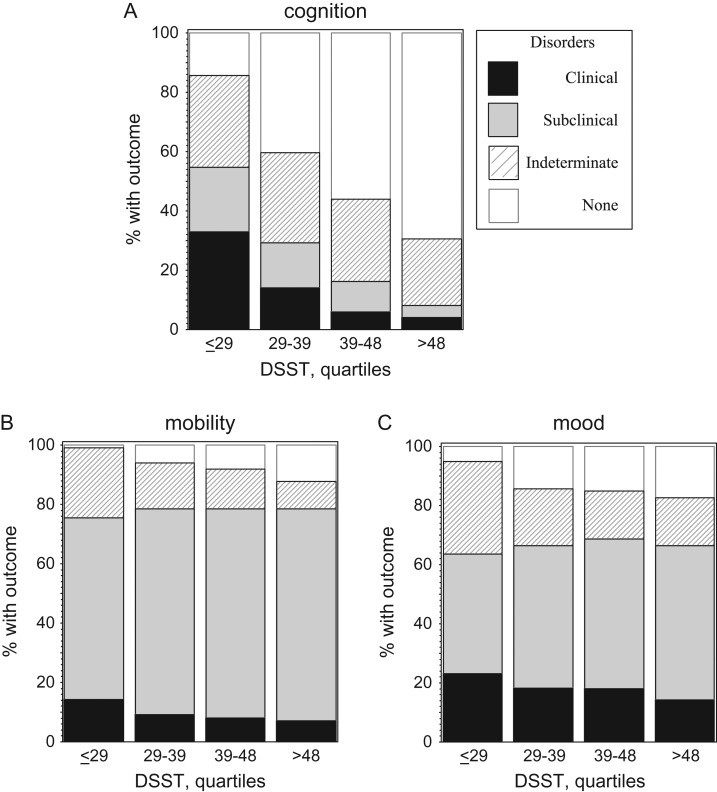
Poor test scores may also be an early biomarker for cognitive decline, decreased activity, and poor mood in old age. Such data were obtained by an international group of scientists in a study involving 5888 people. The generalized results are presented in the graphs:
Image source: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5027641/
Test Applicability in Pharma, Alcohol Dependence and Lack of Sleep
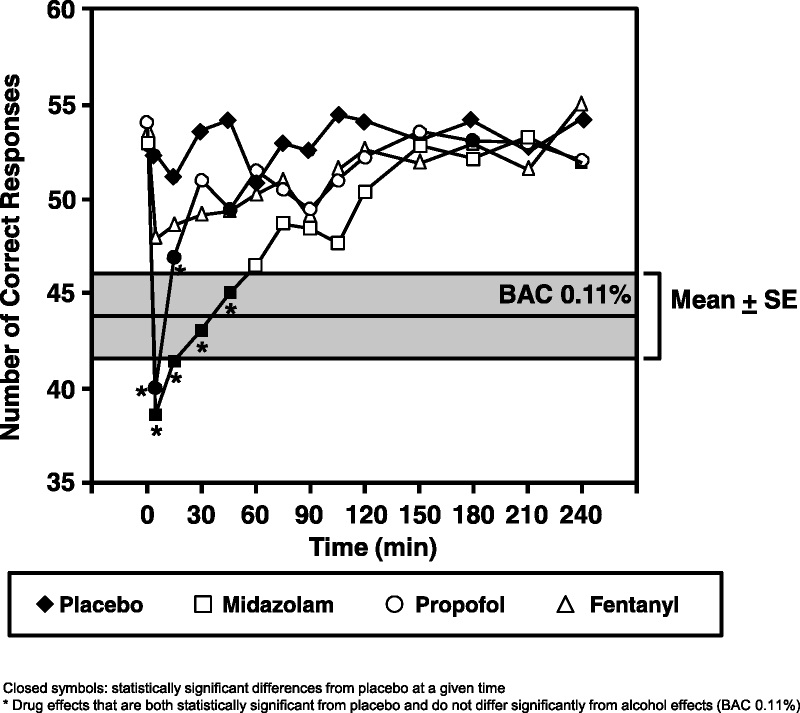
The digital character substitution test has been included in the list of standard tools for studying the pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics of drugs since the 1970s. For example, a study by scientists from the University of Chicago showed that DSST statistically significantly distinguishes the sedative effect of antihistamines from placebo. It also shows the sedative effect of anesthetics for ambulatory surgery. Furthermore, the use of benzodiazepines (drugs used to treat anxiety), insomnia, and seizures significantly worsen test performance compared to placebo:
Image Source: https://journals.lww.com/psychopharmacology/Fulltext/2018/10000/Digit_Symbol_Substitution_Test__The_Case_for.19.aspx
Another study conducted at the University of Spokane (USA) also uses DSST to assess changes in cognitive abilities depending on the duration of sleep. Getting 8 hours of sleep improves performance. 6-hour sleep does not affect the result of the test. However, a 4-hour sleep reduces the result by 12 points after a week:
Image Source: https://journals.lww.com/psychopharmacology/Fulltext/2018/10000/Digit_Symbol_Substitution_Test__The_Case_for.19.aspx
The test shows an interesting pattern in chronic alcoholism. A Boston University study shows that of the many neuropsychological tests, only the DSST was able to measure the brain benefit of long-term (nearly 2 years) abstinence from alcohol compared to short-term (6 weeks) abstinence.
The History of The Test
The Numeric Symbol Replacement Test was initially developed as a research tool for associative learning between 1880 and World War I.
The clinical usefulness of the test was recognized during World War II when it became apparent during examinations of soldiers that the test reliably distinguished brain-damaged patients from healthy ones.
In neuropsychology, the test came into use in 1936 when David Wexler described the test’s sensitivity to brain damage. The scientist also included DSST as a subtest for calculating the intelligence quotient (IQ) on the Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale (WAIS) and children (Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children – WISC). Moreover, the test for substituting digital symbols without significant changes continues to be used in the WAIS scale. For example, in the 2002 version of WAIS IV, the DSST is still the only subtest that detects cognitive impairment and brain damage.
Conclusions
The Digit Symbol Substitution Test (DSST) is a fast and accurate test that identifies cognitive deficits, regardless of the nature of the deficit.
DSST is widely used in clinical practice to detect brain damage, age-related cognitive impairment, and psychiatric disorders.
The test does not depend on the language, culture, or education level. It quickly shows the result and requires a minimum set of tools: a test printout, a pen and a timer.
Useful article, necessary information? Share it!
Someone will also find it useful and necessary:
References
- Digit Symbol Substitution Test. The Case for Sensitivity Over Specificity in Neuropsychological Testing
- Adult Age and Digit Symbol Substitution Performance: A Meta-Analysis
- Clinical correlates of parametric digit-symbol substitution test in schizophrenia
- The Utility of Brief Cognitive Tests for Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review
- Digit Symbol Substitution test and future clinical and subclinical disorders of cognition, mobility and mood in older adults
- Using Alcohol as a Standard to Assess the Degree of Impairment Induced by Sedative and Analgesic Drugs Used in Ambulatory Surgery
- Effects of Sleep Deprivation on Dissociated Components of Executive Functioning
- The relationship between abstinence and Recovery of function in male alcoholics
- From the Binet–Simon to the Wechsler–Bellevue: Tracing the History of Intelligence Testing