Scientists are still looking for antiviral drugs that can be used to treat SARS-CoV-2 infection. Treatment regimens using only one medicine are ineffective. However, the combination of several medications can increase the effectiveness of the treatment while requiring lower dosages than monotherapy and, therefore, causing fewer side effects. In addition, antiviral combinations can prevent the development of SARS-CoV-2 strains resistant to monotherapy.
Previous laboratory studies have identified several combinations that are most effective at suppressing SARS-CoV-2:
- interferon alpha (IFN-α) + remdesivir;
- camostat + remdesivir.
Clinical studies have shown that the following combinations are also effective in suppressing SARS-CoV-2:
Nafamostat (structural analog of camostat) is a short-acting anticoagulant that is also used to treat pancreatitis. It is currently in clinical trials for the treatment of COVID-19.
Clinical studies have shown the effectiveness of IFN-α and its pegylated forms for treating patients with COVID-19.
Norwegian scientists have investigated the effectiveness of a combination of pegylated IFN-α and nafamostat to treat SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus. The efficacy of the drugs was tested on epithelial cells of the lungs of humans and Syrian hamsters.
Pegylated IFN-α and Nafamostat Effectively Suppress SARS-CoV-2 in Human Lung Epithelial Cells
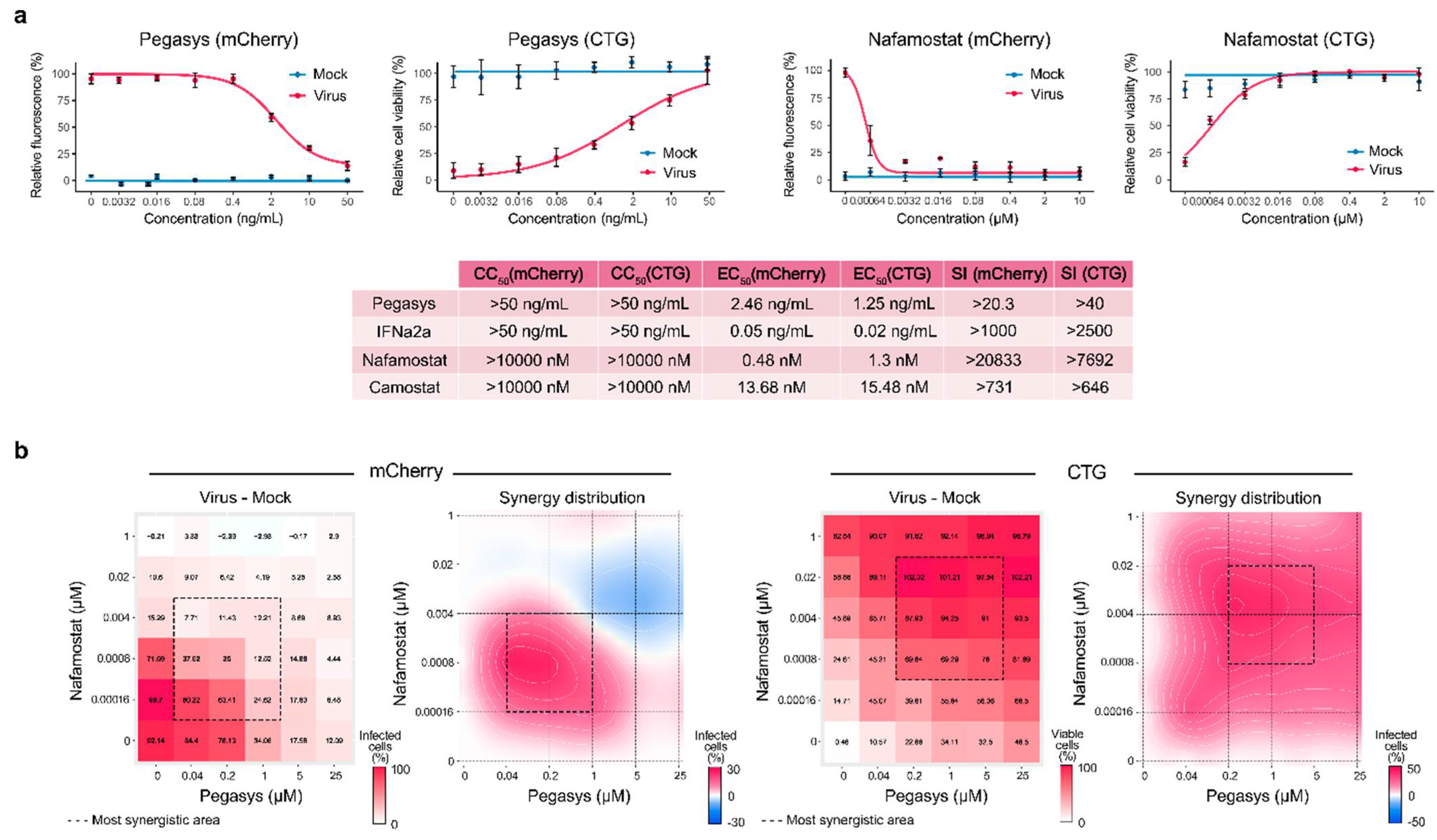
Both pegylated IFN-α and nafamostat reduced SARS-CoV-2 replication in lung epithelial cells and saved cells from death (Fig. 1a). At the same time, pegylated IFN-α reduced the recurrence of SARS-CoV-2 less effectively than its non-pegylated analog, and nafamostat reduced the replication of SARS-CoV-2 more effectively than camostat.
Figure 1. The combination of nafamostat + interferon alfa suppresses SARS-CoV-2 infection in vitro. The graphs show the viability of the virus and the viability of infected cells when treated with pegylated IFN-α and nafamostat:
Combined Interferon-Alpha With Nafamostat Protects Lung Cells at Lower Concentrations than Are Required For Monotherapy
Scientists have observed a strong synergy of the combination of IFN-α + nafamostat. This synergy indicates that both components can be combined in vitro at reduced concentrations to achieve antiviral efficacy comparable to that of individual drugs at high concentrations.
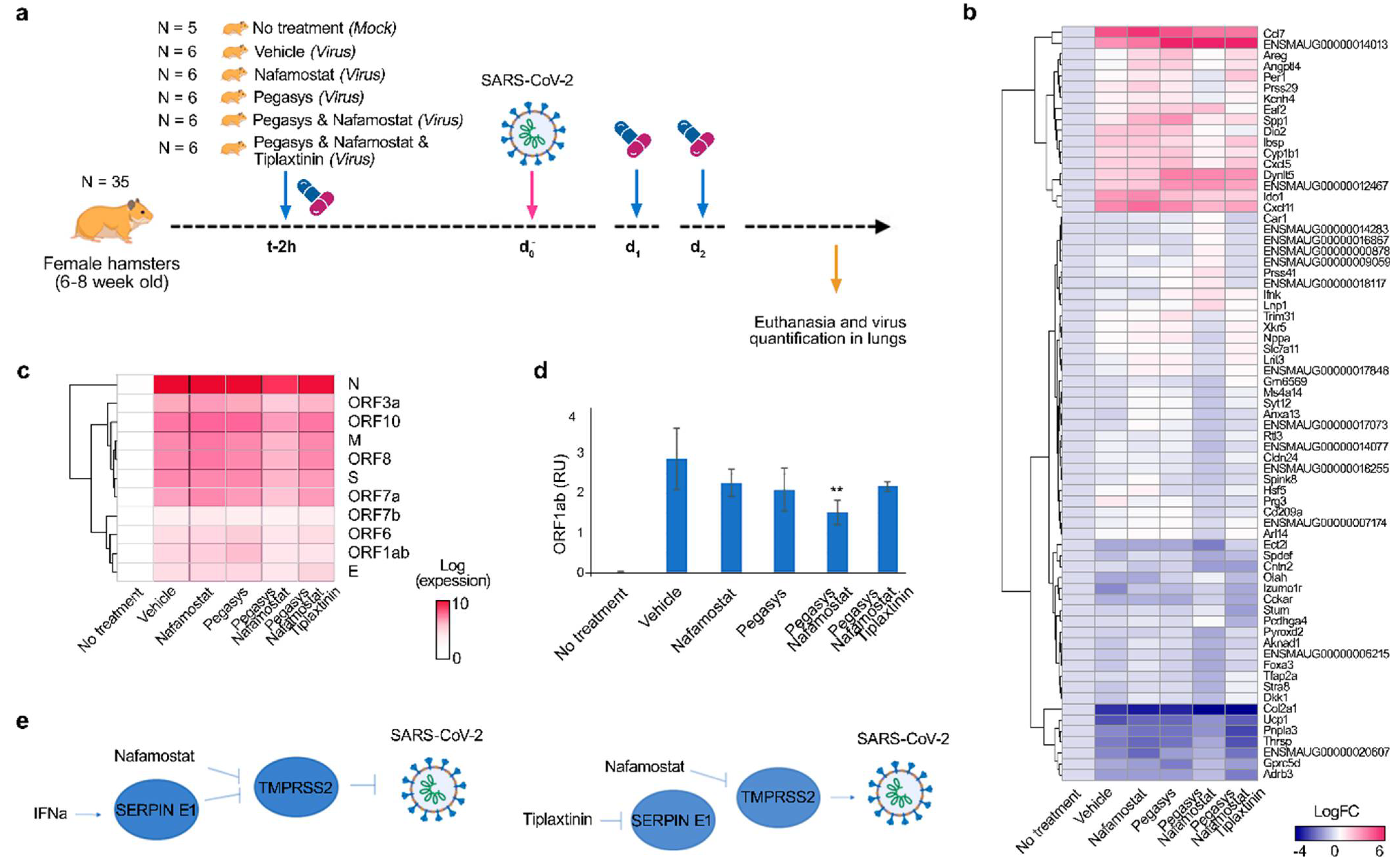
Hamster Experience: The Combination of Interferon-Alpha with Nafamostat Suppresses The Replication of SARS-Cov-2 In Vivo
For the study, the scientists used four groups of Syrian hamsters. On days 0, 1, and 2 of infection, they were injected with:
- Group 1: 40 μg / kg of pegylated IFN-α;
- group 2: 10 mg / kg of nafamostat;
- Group 3: a combination of pegylated IFN-α with nafamostat;
- 4 group: placebo.
On day 0, 2 hours after administration of the drug, the animals were intranasally infected with SARS-CoV-2. The control group remained untreated and uninfected.
The researchers found that the combination of pegylated IFN-α with nafamostat effectively attenuated viral RNA synthesis and virus-induced expression of genes encoding immunomodulatory and neuromodulating proteins (Fig. 2c).
Figure 2. Nafamostat-interferon-alpha combination suppresses SARS-CoV-2 infection in vivo:
What Is The Reason for The Synergistic Effect of Nafamostat and Interferon-Alpha
In the epithelial cells of the lungs and lung organelles, IFN-α activates the transcription of many genes, including SERPINE1. Serpin E1 suppresses the expression of the TMPRSS2 enzyme, which is required for SARS-CoV-2 to enter the cell. Nafamostat also suppresses the expression of TMPRSS2. Thus, the synergy of the combination of IFN-α with nafamostat can be explained because both drugs target TMPRSS2.
The following experience confirms this: when hamsters were injected with the Serpin E1 inhibitor together with IFN-α and nafamostat, the synthesis of viral RNA was restored to the level of one nafamostat. The administration of the Serpin E1 inhibitor completely abolished the effect of IFN-α (Fig. 2c).
Serpin E1 is an essential mediator of IFN-α activity. TMPRSS2 can be treated with a combination of drugs to suppress viral infection synergistically.
Combined Interferon-Alpha with Nafamostat Reduces The Side Effects of These Drugs
Nafamostat reduces the likelihood of thrombosis associated with severe COVID-19. In contrast, interferon-alpha-induced Serpin E1 expression is a risk factor for thrombosis. Thus, when administered together, the anticoagulant properties of nafamostat can compensate for the side effects of IFN-α-induced Serpin E1 expression.
Moreover, a combination therapy containing lower doses of IFN-α and nafamostat can significantly reduce the likelihood of developing other side effects.
Conclusions
The combination of interferon-alpha with nafamostat suppresses SARS-CoV-2 in vitro and in vivo. When administered together, these drugs have a synergistic effect, and to achieve a therapeutic effect, and lower concentrations are needed than monotherapy. Therefore, the side effects of combination therapy are lower.
The introduction of interferon-alpha in combination with a nafamostat may be an effective strategy for treating patients with COVID-19. Further research into the combination of these drugs could help treat many viruses that depend on TMPRSS2 for replication, including influenza viruses and other coronaviruses.
Useful article, necessary information? Share it!
Someone will also find it useful and necessary: