Reprofiling of medicines in medical practice
The COVID-19 pandemic has forced the global medical community to rush to find effective prevention and treatment methods and treat a new coronavirus infection. The goal is to reduce morbidity and mortality.
Developing and implementing new drugs in clinical practice is a long process, measured in months and years. Therefore, since the beginning of the pandemic, the practise of repurposing existing drugs for the treatment of COVID-19 has been widely used. For example, antimalarials are included in treatment protocols for coronavirus infection in many countries around the world.
There are already several cases of successful drug conversion in medical science. The most famous is the sedative sleeping drug thalidomide for the treatment of a malignant tumor — multiple myeloma.
Traditional use of statins
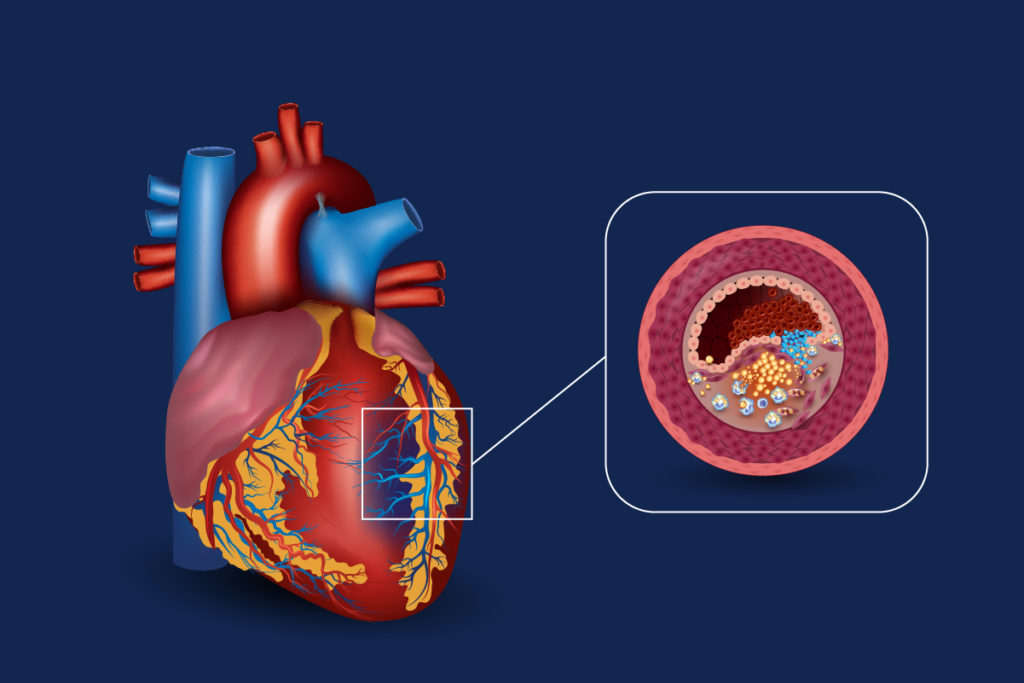
Statins are cholesterol-lowering medications. They treat atherosclerosis and prevent cardiovascular complications.
These drugs prevent the formation of atherosclerotic plaques, which reduce the lumen of blood vessels and stimulate blood clots’ formation. Anti-cholesterol drugs inhibit the body’s synthesis of very-low-density lipoproteins, which make up plaques.
Systemic role of statins in coronavirus disease
Positive effect
Statins have some essential properties that facilitate the course of COVID-19.
These drugs can regulate an immune activity. With COVID-19, a cytokine storm occurs due to the immune system’s hyperactivity, which leads to the destruction of body tissues. Statins reduce the risk of a cytokine storm.
Statins have an anti-inflammatory effect, modulating the production of Pro-inflammatory proteins-cytokines. Some severe patients with coronavirus infection are treated with heparin to reduce the formation of blood clots. This class of drugs also has antithrombotic functions and can reduce acute lung damage in the disease.
Mixed effect
One of the features of statins is an increase in the activity of the ACE2 cell receptor.
The coronavirus uses this receptor to enter a healthy cell. Therefore, increased activity of the receptor increases the susceptibility to coronavirus infection.
On the other hand, the ACE2 receptor promotes the production of substances that have anti-inflammatory, vasodilating, and antifibrotic effects. These properties facilitate the course of the disease.
The suppression of ACE2 activity leads to severe respiratory failure.
Additional research will reveal the conditions and limitations of statin use in clinical practice.
Statins direct effects on COVID-19
The mechanism of direct antiviral effects of statins on SARS-CoV-2 was predicted using molecular modeling. Calculations have shown that statins can bind to the virus’s main enzyme and, thus, prevent the virus from entering healthy cells and multiplying there.
The binding energy of the virus enzyme was different for different types of statins. Also, depending on the specific anti-cholesterol drug, the number of hydrogen bonds between the statin itself and the virus’s amino acids differed.
As a result, some of these drugs proved to be more effective inhibitors of the main SARS-CoV-2 protease than protease inhibitor drugs.
The encouraging results of this simulation have not yet been confirmed experimentally.
In observational studies, statins reduce the risk of severe coronavirus disease
Even at the beginning of the pandemic, doctors in different countries noted that people who continuously take anti-cholesterol medications are less likely to be admitted to intensive care units.
People who continuously take statins suffer from hypertension, diabetes, chronic kidney disease, and obesity if these people stop taking the drug, the risk of coronary heart disease and its complications increases.
Doctors from Wuhan University (China) conducted an observational study of 13,891 patients with COVID-19, of whom 1,219 were regularly taking statins. It was found that for people who did not take drugs in this class, the risk of death from coronavirus was 9.4%. Moreover, for people who were continually taking statins, it was 5.2%.
Doctors from the University of California (USA) in a similar observational study examined the medical records of 5281 patients admitted to the University clinic. The result was similar: when taking statins, the risk of developing severe COVID-19 was more than halved, and patients recovered faster.
It is important to note that observational studies provide only a general idea of the potential effect of drugs on clinical outcomes. This type of research is subject to a high risk of systematic error that does not allow you to determine the observed phenomenon’s cause. Additional randomized controlled trials are required to confirm the results before introducing the new method into General medical practice.
For example, in 2014, there was already a situation when observational studies showed that statins reduce sepsis mortality. Furthermore, randomized controlled trials did not reveal this causal relationship.
Contraindications and side effects of statins
Statins are prescription drugs and are used as prescribed by a doctor.
Instructions for these drugs contain an extensive list of contraindications and side effects. Here are some of them.
Contraindications:
- liver diseases in the active phase;
- under 18 years of age;
- pregnancy and breastfeeding;
- lactose intolerance.
Side effects:
- type 2 diabetes;
- headache, dizziness;
- abdominal pain, nausea, constipation;
- pancreatitis;
- myalgia;
- asthenic syndrome;
- proteinuria, acute renal failure;
- thrombocytopenia.
Conclusions
Randomized controlled trials should confirm the encouraging results of observational studies on the benefits of statins in coronavirus. However, during a pandemic, a decision on using this class of drugs may be made based on the risk-benefit ratio even before the final research results are available.
However, the authors of observational studies warn against hasty, inappropriate use of statins to prevent and treat COVID-19.
It remains an open question of whether anti-cholesterol drugs will be useful for treating coronavirus infection if a person has never taken these drugs.
Sources:
- Teaching Old Drugs New Tricks: Statins for COVID-19?
- Relation of Statin Use Prior to Admission to Severity and Recovery Among COVID-19 Inpatients
- Statins and the COVID-19 main protease: in silico evidence on direct interaction